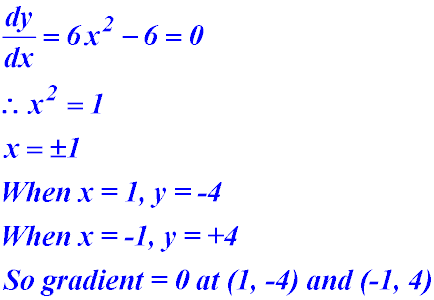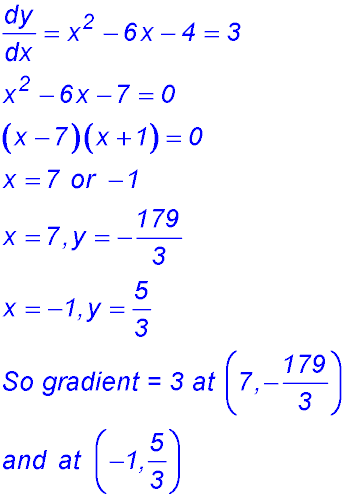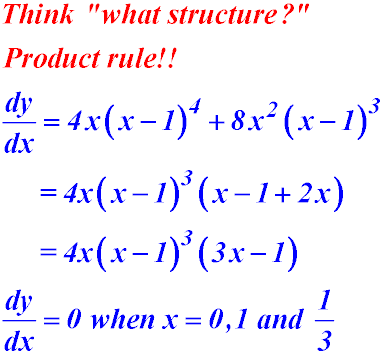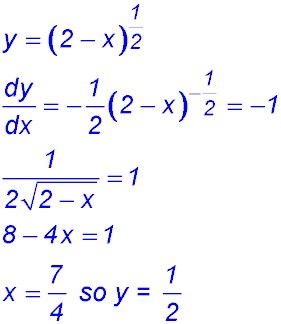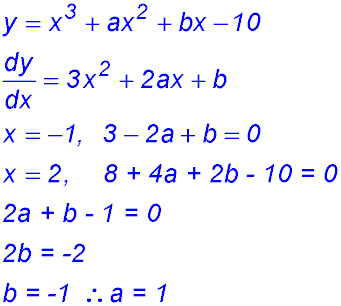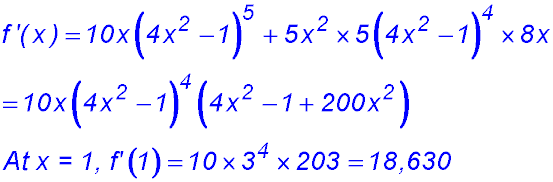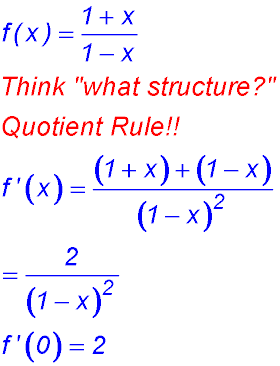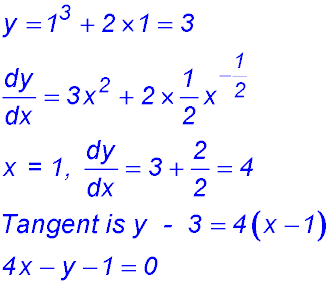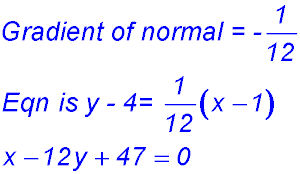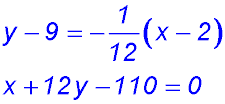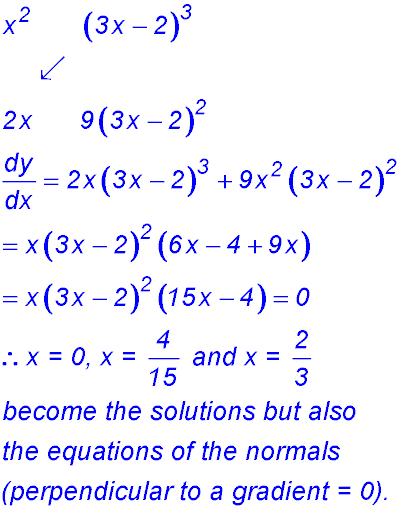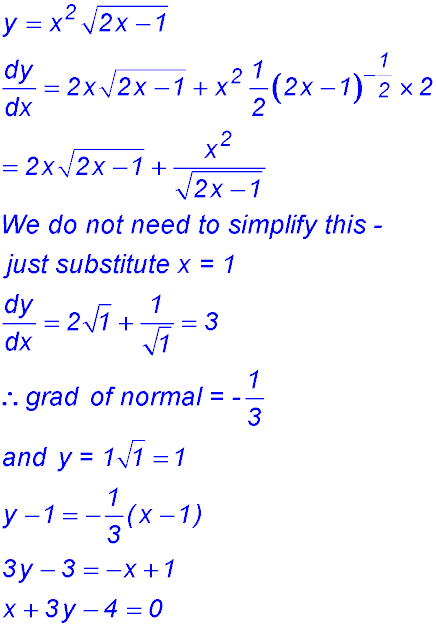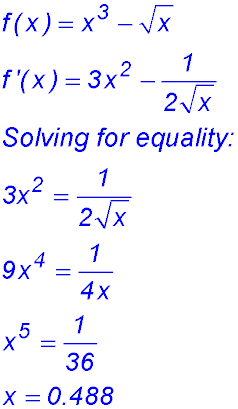Where the techniques of Maths
are explained in simple terms.
Calculus - Differentiation - First derivative.
Gradients and equations of curves, tangents, etc - Test Yourself 1 - Solutions.
- Algebra & Number
- Calculus
- Financial Maths
- Functions & Quadratics
- Geometry
- Measurement
- Networks & Graphs
- Probability & Statistics
- Trigonometry
- Maths & beyond
- Index
Remember that the first derivative is the gradient function of an original function.
So it is used to answer questions requiring information about the slope of a curve.
| Gradients | 1. y = 2x3 - 6x where gradient equals zero?
|
2. 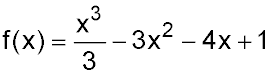 - gradient equals 3?
- gradient equals 3?
|
|
| 3. At what value(s) of x does the curve
y = 2x2 (x - 1)4 have its gradient equal to zero?
|
4. At what point on the curve does the gradient equal -1?
|
||
| 5. y = x3 + ax2 + bx - 10 cuts the x-axis at x = 2 and it has a gradient of zero at x = -1.
|
6. Evaluate f '(1) if f(x) = 5x2(4x2 - 1)5.
|
||
| 7. f(x) = x2 + x
f '(x) = 2x + 1 f"(x) = 2 ∴ x2 + x = 2 x2 + x - 2 = 0 (x + 2)(x - 1) = 0 x = -2 or +1 y = 5 or 3 Points are (-2, 5) or (1, 3). |
8. 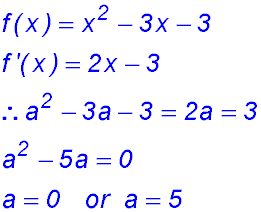 |
||
9. Evaluate f '(0) if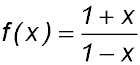 . .
|
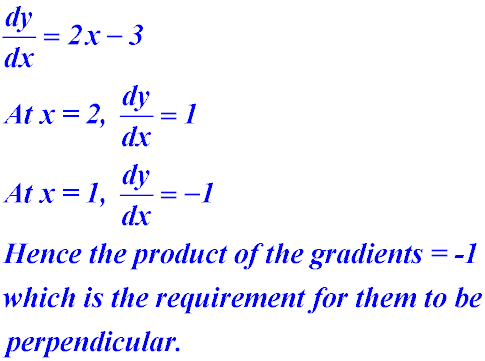
10. Prove that the tangents at the points (2, -3) and (1, -3) on the curve y = x2 - 3x -1 are perpendicular to one another.
|
||
| 11. y = ax2 + bx (i)
y' = 2ax + b (ii) At the point (2, 1) Sub into (i): 1 = 4a + 2b Sub into (ii): -8 = 4a + b Solve simultaneously - subtract (i) - (ii): 9 = b a = -17/4 = -4.25 ∴ a = -17/4 and b = 9. |
12. f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
f '(x) = 2ax + b Substituting given values: a = a + b + c so b = -c 1 = 2a + b 1 = 2a -c ∴ a = (1 + c)/2 |
||
| Points of contact | 13. The gradient of a tangent to the curve
y = x2 - 5x is -3. Find the coordinates of the point of contact of the tangent to the curve . y' = 2x - 5 = -3 x = 1 and so y = -4. |
14. The gradient of a tangent to the curve
y = x2 + 7x - 3 is 9. Find the coordinates of the point of contact of the tangent to the curve. y' = 2x + 7 = 9 x = 1 and so y = 5. |
|
15. y = x2 - 2x - 8 has gradient 8 and its equation is y = ax + b.
|
16. 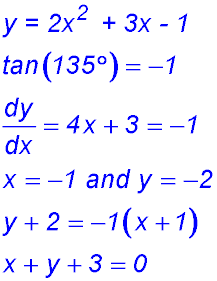 |
||
| 17. For y = 2x - 5 the gradient is 2.
For y = x2 + bx + 4 the gradient function is y ' = 2x + b. At x = 3, the gradients are the same. So: 2 = 6 + b b = -4. |
18. 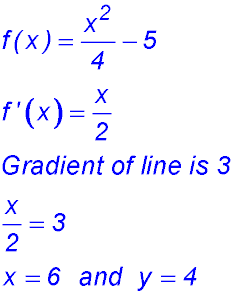 |
||
| Equations of tangents & normals. | Ordinary derivative. | 19. Find the equation of the normal
to the curve y = 3x - 2x2 at x = 1.
|
20. Find the equation of the tangent to the curve where x = 1.
|
21. The curve y = ax2 - 2x -14 has a gradient of 10 when x = 2. Find the value of a.
|
22. Find the equation of the tangent to y = 3x4 + 1 at the point (1, 4). y' = 12x3 At x = 1, y' = 12
|
||
23. (i)
|
24. 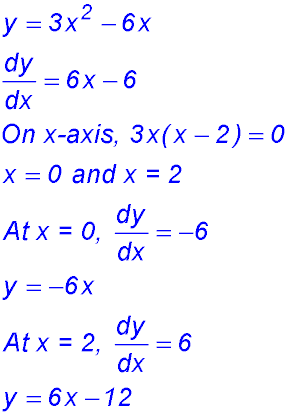 |
||
| Chain rule. | 25.Find the equation of the tangent to
y = (2x - 3)2 at the point where x = 3.
|
26. Find the equation of the normal to the curve f(x) = (2x - 1)2 at x = 2.
|
|
| Product rule. | 27. y = x2 (3x - 2)3
|
28. 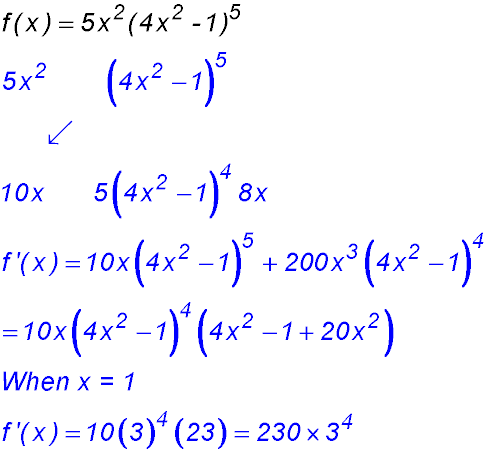 |
|
| 29.
|
30. 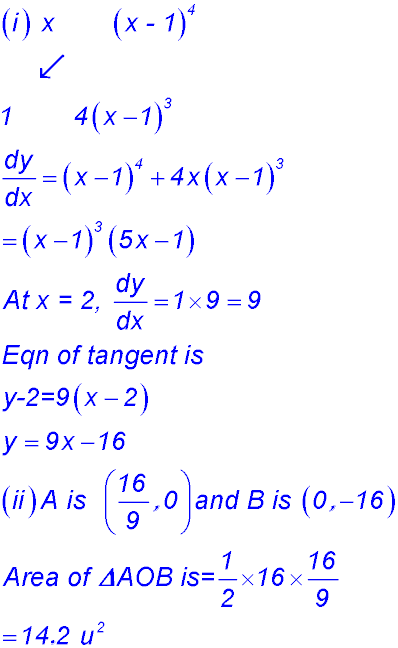 |
||
| Quotient rule. | 31. 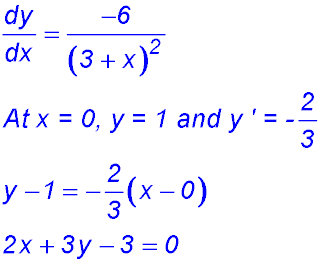 |
32. 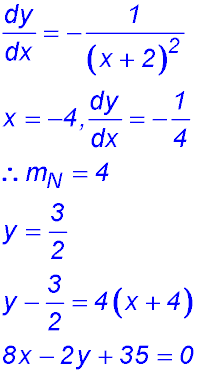 |
|
| Increasing/ decreasing functions. | 33. For what values of x is the function f(x) = 6 - 3x - x2 increasing?
To be increasing, the function f '(x) = -3 - 2x > 0 2x < -3 x < -1.5
|
34. For what values of x is the function
f(x) = x3 + x2 - 5x - 6 decreasing? f '(x) = 3x2 + 2x - 5 = (3x + 5) (x - 1) x = -5/3 or x = 1 To be a decreasing function, f '(x) < 0 Testing on a number line: f '(0) = -5 < 0 So -5/3 < x < 1
|
|
35. 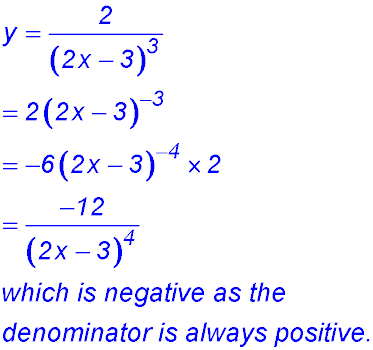
∴ function is monotonically decreasing for all x ≠ 1.5 |
36. The function is not defined for x < 0 and the derivative is not defined at x = 0. So the function is decreasing for 0 < x < 0.488. |
||
| Applications to points of intersection, area, etc | 37. y = 8 - 2x2
|
||
| 38. y = x + 3 and y = 5x - x2.
(i) For POI, x + 3 = 5x - x2 x2 - 4x + 3 = 0 (x - 3)(x - 1) = 0 giving x = 3 and x = 1 When x = 3, y = 6 and when x = 1, y = 4. So P is (3, 6) and Q is (1, 4). (ii) y ' = 5 - 2x So gradient at P = 5 - 2(3) = -1 and at Q = 5 - 2(1) = 3. ∴ Eqn of tangent at P is x + y - 9 = 0 and eqn of tangent at Q is 3x - y + 1= 0. (iii) At A, P meets the y axis at y = 9 and at B, Q meets the y axis at 1. Distance between A and B = 9 - 1 = 8 units.
|
|||
39. 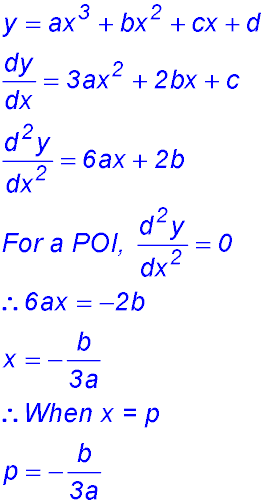 |
|||